README.md
# Python Video Stabilization <img src='https://s3.amazonaws.com/python-vidstab/logo/vidstab_logo_hex.png' width=125 align='right'/>
<!-- noop -->
[](https://travis-ci.org/AdamSpannbauer/python_video_stab)
[](https://codecov.io/gh/AdamSpannbauer/python_video_stab)
[](https://codeclimate.com/github/AdamSpannbauer/python_video_stab/maintainability)
[](https://pypi.org/project/vidstab/)
[](https://github.com/AdamSpannbauer/python_video_stab/commits/master)
[](https://pepy.tech/project/vidstab)
Python video stabilization using OpenCV. Full [searchable documentation here](https://adamspannbauer.github.io/python_video_stab).
This module contains a single class (`VidStab`) used for video stabilization. This class is based on the work presented by Nghia Ho in [SIMPLE VIDEO STABILIZATION USING OPENCV](http://nghiaho.com/?p=2093). The foundation code was found in a comment on Nghia Ho's post by the commenter with username koala.
Input | Output
:-------------------------------:|:-------------------------:
 | 
*[Video](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9pypPqbV_GM) used with permission from [HappyLiving](https://www.facebook.com/happylivinginfl/)*
## Contents:
1. [Installation](#installation)
* [Install `vidstab` without installing OpenCV](#install-vidstab-without-installing-opencv)
* [Install vidstab & OpenCV](#install-vidstab-opencv)
2. [Basic Usage](#basic-usage)
* [Using from command line](#using-from-command-line)
* [Using VidStab class](#using-vidstab-class)
3. [Advanced Usage](#advanced-usage)
* [Plotting frame to frame transformations](#plotting-frame-to-frame-transformations)
* [Using borders](#using-borders)
* [Using Frame Layering](#using-frame-layering)
* [Stabilizing a frame at a time](#stabilizing-a-frame-at-a-time)
* [Working with live video](#working-with-live-video)
* [Transform File Writing & Reading](#transform-file-writing--reading)
## Installation
> ```diff
> + Please report issues if you install/try to install and run into problems!
> ```
### Install `vidstab` without installing OpenCV
If you've already built OpenCV with python bindings on your machine it is recommended to install `vidstab` without installing the pypi versions of OpenCV. The `opencv-python` python module can cause issues if you've already built OpenCV from source in your environment.
The below commands will install `vidstab` without OpenCV included.
#### From PyPi
```bash
pip install vidstab
```
#### From GitHub
```bash
pip install git+https://github.com/AdamSpannbauer/python_video_stab.git
```
### Install `vidstab` & OpenCV
If you don't have OpenCV installed already there are a couple options.
1. You can build OpenCV using one of the great online tutorials from [PyImageSearch](https://www.pyimagesearch.com/), [LearnOpenCV](https://www.learnopencv.com/), or [OpenCV](https://docs.opencv.org/3.0-beta/doc/py_tutorials/py_setup/py_table_of_contents_setup/py_table_of_contents_setup.html#py-table-of-content-setup) themselves. When building from source you have more options (e.g. [platform optimization](https://www.pyimagesearch.com/2017/10/09/optimizing-opencv-on-the-raspberry-pi/)), but more responsibility. Once installed you can use the pip install command shown above.
2. You can install a pre-built distribution of OpenCV from pypi as a dependency for `vidstab` (see command below)
The below commands will install `vidstab` with `opencv-contrib-python` as dependencies.
#### From PyPi
```bash
pip install vidstab[cv2]
```
#### From Github
```bash
pip install -e git+https://github.com/AdamSpannbauer/python_video_stab.git#egg=vidstab[cv2]
```
## Basic usage
The `VidStab` class can be used as a command line script or in your own custom python code.
### Using from command line
```bash
# Using defaults
python3 -m vidstab --input input_video.mov --output stable_video.avi
```
```bash
# Using a specific keypoint detector
python3 -m vidstab -i input_video.mov -o stable_video.avi -k GFTT
```
### Using `VidStab` class
```python
from vidstab import VidStab
# Using defaults
stabilizer = VidStab()
stabilizer.stabilize(input_path='input_video.mov', output_path='stable_video.avi')
# Using a specific keypoint detector
stabilizer = VidStab(kp_method='ORB')
stabilizer.stabilize(input_path='input_video.mp4', output_path='stable_video.avi')
# Using a specific keypoint detector and customizing keypoint parameters
stabilizer = VidStab(kp_method='FAST', threshold=42, nonmaxSuppression=False)
stabilizer.stabilize(input_path='input_video.mov', output_path='stable_video.avi')
```
## Advanced usage
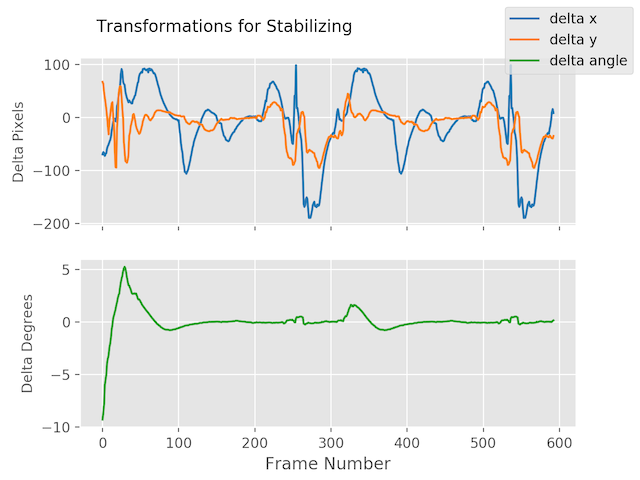
### Plotting frame to frame transformations
```python
from vidstab import VidStab
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
stabilizer = VidStab()
stabilizer.stabilize(input_path='input_video.mov', output_path='stable_video.avi')
stabilizer.plot_trajectory()
plt.show()
stabilizer.plot_transforms()
plt.show()
```
Trajectories | Transforms
:-------------------------------:|:-------------------------:
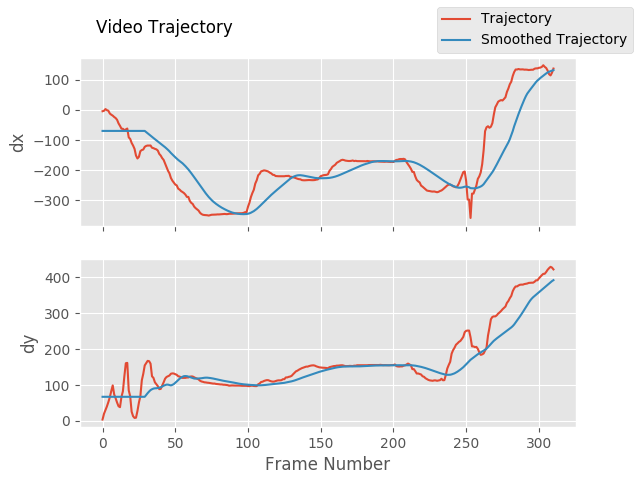 | 
### Using borders
```python
from vidstab import VidStab
stabilizer = VidStab()
# black borders
stabilizer.stabilize(input_path='input_video.mov',
output_path='stable_video.avi',
border_type='black')
stabilizer.stabilize(input_path='input_video.mov',
output_path='wide_stable_video.avi',
border_type='black',
border_size=100)
# filled in borders
stabilizer.stabilize(input_path='input_video.mov',
output_path='ref_stable_video.avi',
border_type='reflect')
stabilizer.stabilize(input_path='input_video.mov',
output_path='rep_stable_video.avi',
border_type='replicate')
```
<table>
<tr>
<td><p align='center'><code>border_size=0</code></p></td>
<td><p align='center'><code>border_size=100</code></p></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td><p align='center'><img src='https://s3.amazonaws.com/python-vidstab/readme/stable_ostrich.gif'></p></td>
<td><p align='center'><img src='https://s3.amazonaws.com/python-vidstab/readme/wide_stable_ostrich.gif'></p></td>
</tr>
</table>
`border_type='reflect'` | `border_type='replicate'`
:--------------------------------------:|:-------------------------:
 | 
*[Video](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9pypPqbV_GM) used with permission from [HappyLiving](https://www.facebook.com/happylivinginfl/)*
### Using Frame Layering
```python
from vidstab import VidStab, layer_overlay, layer_blend
# init vid stabilizer
stabilizer = VidStab()
# use vidstab.layer_overlay for generating a trail effect
stabilizer.stabilize(input_path=INPUT_VIDEO_PATH,
output_path='trail_stable_video.avi',
border_type='black',
border_size=100,
layer_func=layer_overlay)
# create custom overlay function
# here we use vidstab.layer_blend with custom alpha
# layer_blend will generate a fading trail effect with some motion blur
def layer_custom(foreground, background):
return layer_blend(foreground, background, foreground_alpha=.8)
# use custom overlay function
stabilizer.stabilize(input_path=INPUT_VIDEO_PATH,
output_path='blend_stable_video.avi',
border_type='black',
border_size=100,
layer_func=layer_custom)
```
`layer_func=vidstab.layer_overlay` | `layer_func=vidstab.layer_blend`
:--------------------------------------:|:-------------------------:
 | 
*[Video](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9pypPqbV_GM) used with permission from [HappyLiving](https://www.facebook.com/happylivinginfl/)*
### Automatic border sizing
```python
from vidstab import VidStab, layer_overlay
stabilizer = VidStab()
stabilizer.stabilize(input_path=INPUT_VIDEO_PATH,
output_path='auto_border_stable_video.avi',
border_size='auto',
# frame layering to show performance of auto sizing
layer_func=layer_overlay)
```
<p align='center'>
<img width='45%' src='https://s3.amazonaws.com/python-vidstab/readme/auto_border_stable_ostrich.gif'>
</p>
### Stabilizing a frame at a time
The method `VidStab.stabilize_frame()` can accept `numpy` arrays to allow stabilization processing a frame at a time.
This can allow pre/post processing for each frame to be stabilized; see examples below.
#### Simplest form
```python
from vidstab.VidStab import VidStab
stabilizer = VidStab()
vidcap = cv2.VideoCapture('input_video.mov')
while True:
grabbed_frame, frame = vidcap.read()
if frame is not None:
# Perform any pre-processing of frame before stabilization here
pass
# Pass frame to stabilizer even if frame is None
# stabilized_frame will be an all black frame until iteration 30
stabilized_frame = stabilizer.stabilize_frame(input_frame=frame,
smoothing_window=30)
if stabilized_frame is None:
# There are no more frames available to stabilize
break
# Perform any post-processing of stabilized frame here
pass
```
#### Example with object tracking
```python
import os
import cv2
from vidstab import VidStab, layer_overlay, download_ostrich_video
# Download test video to stabilize
if not os.path.isfile("ostrich.mp4"):
download_ostrich_video("ostrich.mp4")
# Initialize object tracker, stabilizer, and video reader
object_tracker = cv2.TrackerCSRT_create()
stabilizer = VidStab()
vidcap = cv2.VideoCapture("ostrich.mp4")
# Initialize bounding box for drawing rectangle around tracked object
object_bounding_box = None
while True:
grabbed_frame, frame = vidcap.read()
# Pass frame to stabilizer even if frame is None
stabilized_frame = stabilizer.stabilize_frame(input_frame=frame, border_size=50)
# If stabilized_frame is None then there are no frames left to process
if stabilized_frame is None:
break
# Draw rectangle around tracked object if tracking has started
if object_bounding_box is not None:
success, object_bounding_box = object_tracker.update(stabilized_frame)
if success:
(x, y, w, h) = [int(v) for v in object_bounding_box]
cv2.rectangle(stabilized_frame, (x, y), (x + w, y + h),
(0, 255, 0), 2)
# Display stabilized output
cv2.imshow('Frame', stabilized_frame)
key = cv2.waitKey(5)
# Select ROI for tracking and begin object tracking
# Non-zero frame indicates stabilization process is warmed up
if stabilized_frame.sum() > 0 and object_bounding_box is None:
object_bounding_box = cv2.selectROI("Frame",
stabilized_frame,
fromCenter=False,
showCrosshair=True)
object_tracker.init(stabilized_frame, object_bounding_box)
elif key == 27:
break
vidcap.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
```
<p align='center'>
<img width='50%' src='https://s3.amazonaws.com/python-vidstab/readme/obj_tracking_vidstab_1.gif'>
</p>
### Working with live video
The `VidStab` class can also process live video streams. The underlying video reader is `cv2.VideoCapture`([documentation](https://docs.opencv.org/3.0-beta/doc/py_tutorials/py_gui/py_video_display/py_video_display.html)).
The relevant snippet from the documentation for stabilizing live video is:
> *Its argument can be either the device index or the name of a video file. Device index is just the number to specify which camera. Normally one camera will be connected (as in my case). So I simply pass 0 (or -1). You can select the second camera by passing 1 and so on.*
The `input_path` argument of the `VidStab.stabilize` method can accept integers that will be passed directly to `cv2.VideoCapture` as a device index. You can also pass a device index to the `--input` argument for command line usage.
One notable difference between live feeds and video files is that webcam footage does not have a definite end point.
The options for ending a live video stabilization are to set the max length using the `max_frames` argument or to manually stop the process by pressing the <kbd>Esc</kbd> key or the <kbd>Q</kbd> key.
If `max_frames` is not provided then no progress bar can be displayed for live video stabilization processes.
#### Example
```python
from vidstab import VidStab
stabilizer = VidStab()
stabilizer.stabilize(input_path=0,
output_path='stable_webcam.avi',
max_frames=1000,
playback=True)
```
<p align='center'>
<img width='50%' src='https://s3.amazonaws.com/python-vidstab/readme/webcam_stable.gif'>
</p>
### Transform file writing & reading
#### Generating and saving transforms to file
```python
import numpy as np
from vidstab import VidStab, download_ostrich_video
# Download video if needed
download_ostrich_video(INPUT_VIDEO_PATH)
# Generate transforms and save to TRANSFORMATIONS_PATH as csv (no headers)
stabilizer = VidStab()
stabilizer.gen_transforms(INPUT_VIDEO_PATH)
np.savetxt(TRANSFORMATIONS_PATH, stabilizer.transforms, delimiter=',')
```
File at `TRANSFORMATIONS_PATH` is of the form shown below. The 3 columns represent delta x, delta y, and delta angle respectively.
```
-9.249733913760086068e+01,2.953221378387767970e+01,-2.875918912994855636e-02
-8.801434576214279559e+01,2.741942225927152776e+01,-2.715232319470826938e-02
```
#### Reading and using transforms from file
Below example reads a file of transforms and applies to an arbitrary video. The transform file is of the form shown in [above section](#generating-and-saving-transforms-to-file).
```python
import numpy as np
from vidstab import VidStab
# Read in csv transform data, of form (delta x, delta y, delta angle):
transforms = np.loadtxt(TRANSFORMATIONS_PATH, delimiter=',')
# Create stabilizer and supply numpy array of transforms
stabilizer = VidStab()
stabilizer.transforms = transforms
# Apply stabilizing transforms to INPUT_VIDEO_PATH and save to OUTPUT_VIDEO_PATH
stabilizer.apply_transforms(INPUT_VIDEO_PATH, OUTPUT_VIDEO_PATH)
```