graph-traversing/README.md
# Graph Traversing/Searching Algorithms
## Breadth-first search (BFS)
Breadth-first search (BFS) is an algorithm for traversing or searching tree or graph data structures. It starts at the tree root (or some arbitrary node of a graph, sometimes referred to as a 'search key'[1]) and explores the neighbor nodes first, before moving to the next level neighbors.
|____ |____ |
|-----------------------------|-----------------|
|Class |Search algorithms|
|Data structure |Graph |
|Worst case performance |`O(|E|)=O(b^{d})`|
|Worst case space complexity |`O(|V|)=O(b^{d})`|
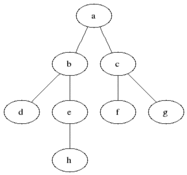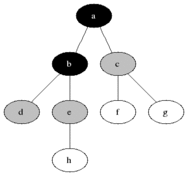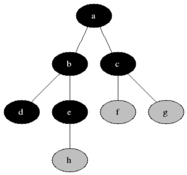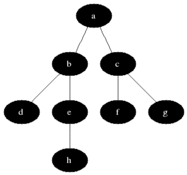
### Pseudocode
*Input:* A graph Graph and a starting vertex root of Graph
*Output:* All vertices reachable from root labeled as explored.
A non-recursive implementation of breadth-first search:
```
Breadth-First-Search(Graph, root):
for each node n in Graph:
n.distance = INFINITY
n.parent = NIL
create empty queue Q
root.distance = 0
Q.enqueue(root)
while Q is not empty:
current = Q.dequeue()
for each node n that is adjacent to current:
if n.distance == INFINITY:
n.distance = current.distance + 1
n.parent = current
Q.enqueue(n)
```
## Depth-first search
Depth-first search (DFS) is an algorithm for traversing or searching tree or graph data structures. One starts at the root (selecting some arbitrary node as the root in the case of a graph) and explores as far as possible along each branch before backtracking.
|____ |____ |
|----------------------------|-----------------|
|Class |Search algorithm |
|Data structure |Graph |
|Worst case performance |`O(|E|)` |
|Worst case space complexity |`O(|V|)` |

### Pseudocode
*Input:* A graph G and a vertex v of G
*Output:* All vertices reachable from v labeled as discovered
A recursive implementation of DFS:
```
procedure DFS(G,v):
label v as discovered
for all edges from v to w in G.adjacentEdges(v) do
if vertex w is not labeled as discovered then
recursively call DFS(G,w)
```
# Additional Resources
#### Graph - Wikipedia
- Link: [Graph (Abstract Data Type) - Wikipedia](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Graph_(abstract_data_type))
- Concepts: *Graph Node*, *Graph theory*, *search* and *depth first search*
#### Depth First Search - Wikipedia
- Link: [Depth First Search - Wikipedia](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Depth-first_search)
- Concepts: *Graph Node*, *Graph theory*, *search* and *depth first search*
#### Breadth First Search - Wikipedia
- Link: [Breadth First Search - Wikipedia](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Breadth-first_search)
- Concepts: *Graph Node*, *Graph theory*, *search* and *breadth first search*
#### The breadth-first search algorithm - Khan Academy
- Link: [The breadth-first search algorithm - Khan Academy](https://www.khanacademy.org/computing/computer-science/algorithms/breadth-first-search/a/the-breadth-first-search-algorithm)
- Concepts: *Trees*, *Data Structures*
#### Labyrinth Algorithms DFS and BFS Visulaization
- Link: [Labyrinth Algorithms DFS and BFS Visulaization](http://bryukh.com/labyrinth-algorithms/)
- Concepts: *Graph Node*, *Graph theory*, *search* and *depth first search*
- Notes: Great site that visualizes BFS and DFS